1 Digital Health Form.
The health form (HF) is one of the most critical and delicate points in the process of underwriting personal insurance such as health insurance. From a fully digital perspective, it requires complex analysis and decision making that goes far beyond moving the paper questionnaire to a web form, which is what most companies that have embarked on the path to digitizing their processes have done so far. We will try to focus on the most relevant points to approach its implementation, taking into account two starting elements:
- The importance of the portfolio of services: The clinical analysis of a particular health questionnaire can result in a subsequent proposal of exclusions, which in the digital health insurance model takes the form of a portfolio of excluded services. This is an important point to which we will dedicate an article of our own in this series, where we will describe the portfolio of services of a health insurance coverage. We anticipate that this is a fundamental armor for the digital management of this line of business and is directly related to the prior assessment of risk.
- The adaptability of the questionnaire: It should also be said that, depending on the level of risk of the coverage, the questionnaire should be different. For example, applying for health insurance without hospitalization is not the same as incorporating this coverage. In digital processes, handling different forms or questionnaires is much easier and more flexible than doing it on paper. Moreover, the questionnaire can be unique, but build it inclusively with different questions – not according to the product requested, but according to the coverage. In other words, it is possible to go into much greater detail and, in this way, gain precision in the information obtained and in the selection of the risk to be taken. A company that handles this type of questionnaire must have insurance software that allows different models to be configured according to the coverage requested.
From a fully digital perspective, the health questionnaire requires complex analysis and decision making that goes far beyond transferring the paper form to a web form,
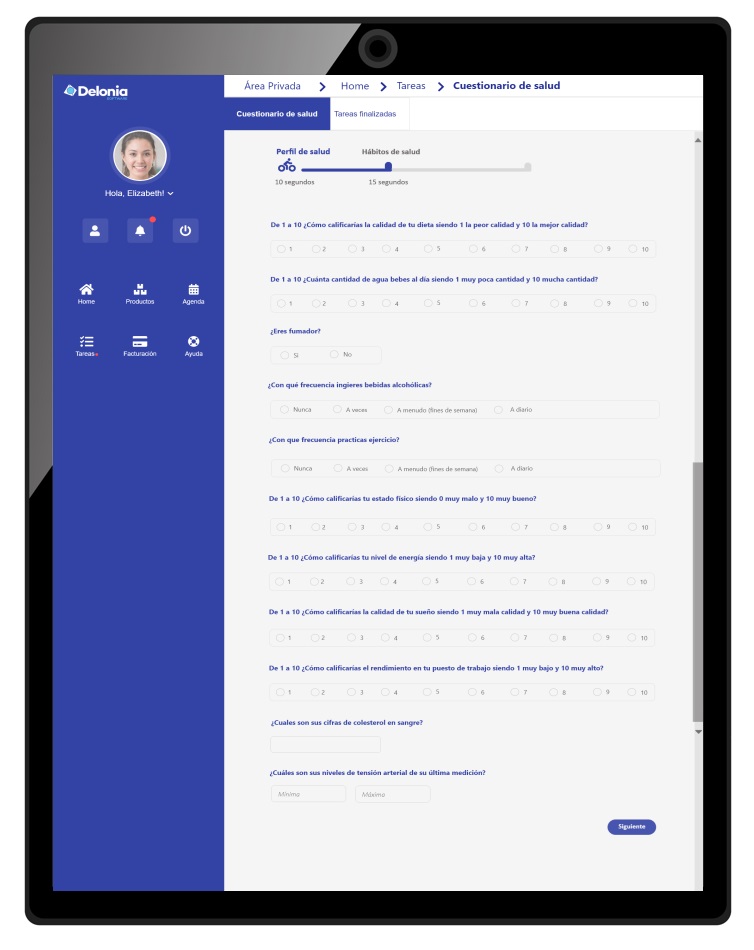
2 Type of questionnaire for risk selection
The different approaches to the level of detail of a health questionnaire naturally have their advantages and disadvantages. We are not going to analyze these details, which are generally determined by parameters such as the marketing channel, channel specialization, marketing campaign or target audience, among others, but we are going to describe them in general terms.
It could be said that there are four possible orientations:
2.1. Detailed health questionnaire:
Of many questions about the client’s health status. If this is the approach, the company should ensure that the answers are test-type and simple (e.g., yes/no or check the appropriate option). Each question should have an associated information icon to explain in detail the meaning and interpretation of the question.
2.2. Short health questionnaire:
It can be reduced to three issues. Inquire into the clinical past (past pathologies), the present (current health status) and the future (if treatment is planned in the near future).. In the affirmative case of any of the questions, you can choose to collect more information through an extended questionnaire or through a semantic assistant that helps the user in the description of the pathologies to which it refers.
2.3. No health questionnaire:
It is certainly a more controversial alternative, but let’s make this reflection. The Insurance Contract Law protects the insurance company. It is well known that no event prior to the contracting of any insurance is covered by it. In the case of health insurance, the client cannot deliberately conceal from the company the diseases or pathologies from which he/she suffers. Strictly speaking, therefore, the health questionnaire should not be necessary as long as it is established that the insured is aware of this point.
Reliably informing the insured of this fact – that their pre-existing conditions will not be covered – and that they accept, even by means of a sworn signature, that they acknowledge and are aware that pre-existing pathologies and treatments are not covered, could be a solution that avoids this procedure and its derivations. The client could also be asked, simply, if he/she believes it is necessary to declare any significant medical condition related to the services to be contracted, stressing that no pre-existing disease will be covered.
To reassure the technical managers in the industry, we can say that in the new digital era we will have new tools to anticipate the detection of pre-existing conditions. This is one of the advantages of the immediacy of information about what is happening in an insurance management software with respect to the benefits system – the subject of another post. Nor should it be forgotten that there are waiting periods on services to minimize the anti-selection of risk.
This model not only protects the company, but also the insured, who sometimes takes out insurance by answering the questionnaire ambiguously or incorrectly – often just out of clumsiness. Subsequently, this can lead the insured to enter into a confrontation with the company for not covering an ailment when, perhaps, he has been paying the premium for some time. The bad reputation of the sector stems from events such as this, and it is therefore very important to reflect on how to improve the selection of risks prior to taking out insurance.

2.4. Health questionnaire conducted by a physician or AI assistant.
The perfect scenario is to have a medical professional conduct the client questionnaire. In this way, he/she will be able to understand the scope of the questions and the physician will be able to inquire into the relevant issues based on the information provided. Why don’t companies use this type of questionnaire if it is the most appropriate? This is done in some types of insurance, for example, for life insurance with high capital sums. However, it is not common practice in health insurance contracting because of the high cost and, above all, because of the complex operational process that must be implemented, with the management of appointments and face-to-face medical evaluations.
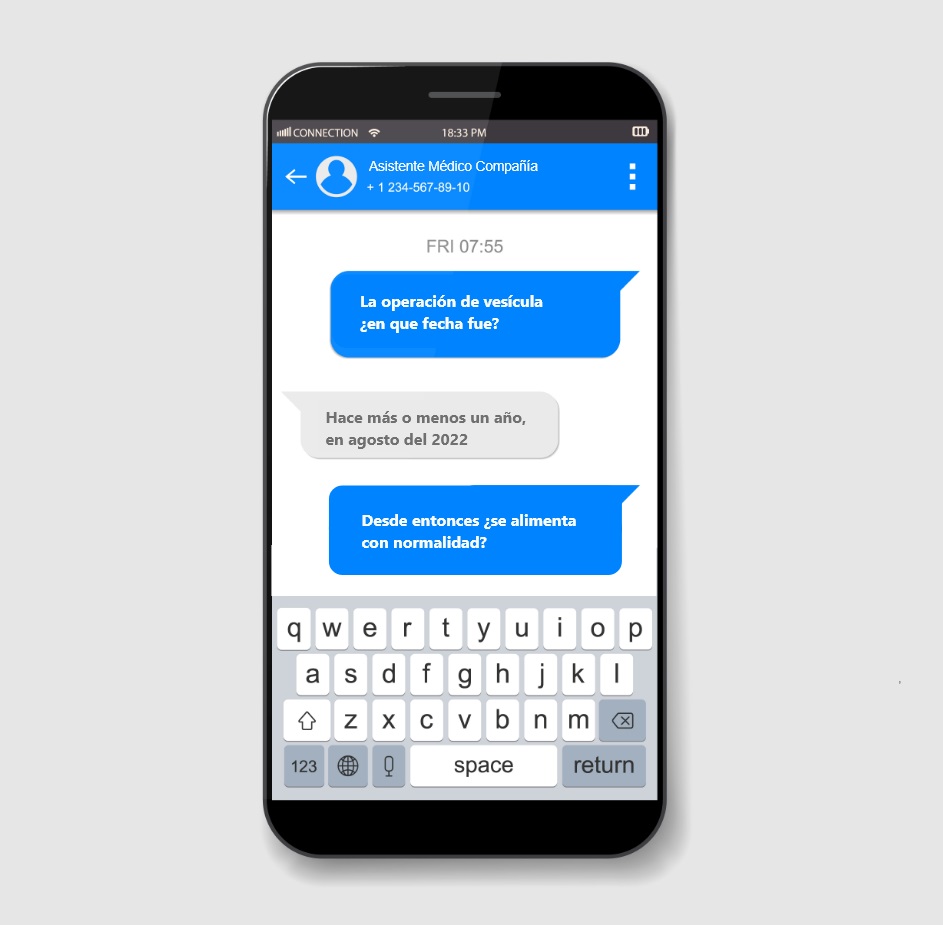
However, through AI models of natural language processing it is possible to reproduce this questionnaire without incurring additional costs. For them, an intelligent conversational virtual doctorchatbot could be used, where the system processes and deepens the questions asked to the customer according to the answer he/she gives.
Through AI models of natural language processing it is possible to reproduce the questionnaire performed by a medical professional.
3 Individual or group questionnaire.
Let’s imagine a customer signing up for health insurance on the company’s website. You are interested in a family policy for several members of your family. When filling out the questionnaire, each of them should complete or at least sign their own. Without going into detail on the issue of the minors and the confidentiality of the process, it does not seem very pragmatic for the whole family to get together to carry out this procedure. A moment of friction in the pursuit of the sale that is worth analyzing. There are two possible solutions to this situation:
- Email: One solution is for the subscriber/insurance policyholder to provide an email address for each of the members who are required to complete the health questionnaire. The process will send to each of them, a link to that email where they will be presented with the health questionnaire that they must answer and sign. The subscription will be stopped until all completed questionnaires are submitted to the company. It would also force the company to design workflows with process milestones: customer reminders, receipt of questionnaire, pending assessment, etc.
- Validation signature: Less rigorous, but a bit more pragmatic, is to have the policyholder fill out the questionnaire on behalf of everyone. In this case, each member would have to verify, confirm and subsequently sign their questionnaire at what point would this action be taken? when the insured accesses the Private Area enabled by the company. In fact, this would be the first action of the Welcome Experience to the insurance company and would be essential for the insured to activate his Private Area.
An important point in insurance underwriting, in a truly digital model supported by a suitable insurance software, is that the management of the signature of the health questionnaires can go in parallel to the process of issuance until the policy is underwritten. The company may issue the policy and not activate the coverage until certain conditions are met or signed in the insured’s Private Area in the welcome process — a relevant moment in the customer’s experience. Thus, in the case of the health questionnaire we are addressing, the company will be able to enable coverage individually when each family member accesses his or her private area and signs the questionnaire that has been submitted.
With this formula, the company will decide the partial/total issue conditions and manage them more precisely.
An important point in the insurance underwriting, in a truly digital model supported by a suitable insurance software, is that the management of the signature of the health questionnaires can go in parallel to the process of issuance until the underwriting of the policy.
4 Semantic Assistant with AI and coding techniques
The major innovation in the digital health questionnaire underwriting process will come from the use of assistants and semantic analysis with Machine Learning techniques. As we have already mentioned, the ideal questionnaire model is one that is assisted by a virtual doctor using an intelligent chatbot with natural language processing (NLP) technology, i.e. a system that understands and processes human conversation, applied to a medical conversation between doctor and patient.
Starting from the design of a first medical questionnaire experience, the machine learning algorithm will allow the system to learn and improve. If at the beginning your assessments will require the final review of a medical professional, the tool will gradually become more reliable until it becomes autonomous.
When requesting information from the user about their pathologies, they will describe them in their own words, not always in technical terms suitable for assessment and underwriting. The semantic assistant based on natural language processing (NLP) will interpret what the client states, proposing concepts and descriptions based on a standardized table of pathologies and treatments, e.g. CIE 9/10/11. This would achieve several objectives:
- Assist the client in completing their health questionnaire with accurate and appropriate terms.
- To have a questionnaire with rigorous, detailed and standardized data.
- Most importantly, the result will be a CODED HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE. This will make it easier to manage risk assessment and apply underwriting rules, either automatically or supervised. We will analyze how this aspect is linked to the excluded services portfolio.
This semantic analyzer can even be applied to a medical report to automatically extract and code the clinical references it contains about a patient.
Obviously, on coded pathologies and treatments it is easy to apply automatic rules that reflect the risk selection criteria that the company wants to apply. In addition, this minimizes the subjective judgment that could occur when a company’s risks are analyzed by different underwriters.
The algorithm developed by artificial intelligence and machine learning will allow the system to learn and improve itself. If at the beginning your assessments will require the final review of a medical professional, the tool will gradually become more reliable until it becomes autonomous.
In conclusion, whichever questionnaire a company chooses to use, it should rely on a virtual assistant to replicate the assessment and questions of a physician and overlay this questionnaire with a layer of semantic analysis to understand, code and encode the answers and information collected in the questionnaire. It is a priority that the current health insurance management software incorporate Artificial Intelligence in: the incremental design of the questions of the questionnaire according to the requested coverage, the dynamic configuration of the questionnaire according to the answers that are given and finally in the analysis and structured coding of the answers. The accuracy that will be gained will not only benefit the company, but also the customer to be insured.






